DEPARTMENT OF NUTRITION AND DIETETICS
A healthy lifestyle consists of eating the right foods, staying away from toxic substances like cigarettes or illicit drugs, and exercising on a consistent basis. Living a healthy lifestyle also requires minimizing stress and having solid relationships.
People sometimes try to lose weight by dieting, which often means cutting out foods and eating fewer calories. However, adding fruits and vegetables in small ways, such as packing fruit for lunch or adding vegetables into dinner recipes, can have beneficial effects on health. Adding healthy foods to a diet is more effective than simply slashing calories. However, it is still important to be aware of daily caloric intake and to avoid eating excessive calories.
Working out does not have to be exhausting or take time out of the day. Taking part in enjoyable physical activities throughout the day can burn calories and aid in weight loss. Taking walks is also an extremely effective way to add exercise into a daily routine. Simple choices, such as parking farther away from buildings, walking around a mall, getting off the bus a few stops early and taking the stairs instead of the elevator, increase the amount of walking and the number of calories burned.


Exercise is safe and highly recommended for most people with type 2 diabetes, including those with complications. Along with diet and medication, exercise will help you lower blood sugar and lose weight. Exercise has so many benefits, but the biggest one is that it makes it easier to control your blood glucose (blood sugar) level. People with type 2 diabetes have too much glucose in their blood, either because their body doesn’t produce enough insulin to process it, or because their body doesn’t use insulin properly (insulin resistant).
In either case, exercise can reduce the glucose in your blood. Muscles can use glucose without insulin when you’re exercising. In other words, it doesn’t matter if you’re insulin resistant or if you don’t have enough insulin: when you exercise, your muscles get the glucose they need, and in turn, your blood glucose level goes down.
If you’re insulin resistant, exercise actually makes your insulin more effective. That is your insulin resistance goes down when you exercise, and your cells can use the glucose more effectively. Exercise can also help people with type 2 diabetes avoid long-term complications, especially heart problems. People with diabetes are susceptible to developing blocked arteries (arteriosclerosis), which can lead to a heart attack.
- Lower blood pressure
- Better control of weight
- Increased level of good cholesterol (HDL)
- Leaner, stronger muscles
- Stronger bones
- More energy
- Improved mood
- Better sleep
- Stress management
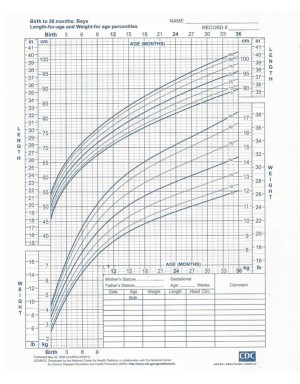
HEIGHT / WEIGHT CHART
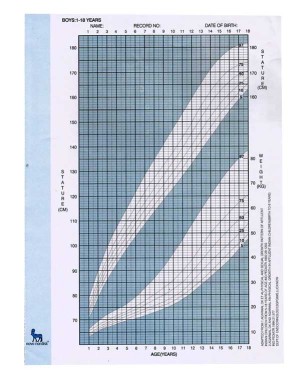
Average height and weight of boys at different ages
(Source : Nutrient Requirements and Recommended Dietary Allowances for Indians, I.C.M.R. 1990.)
| Age | Weight (kg) | Height (cm) |
| Birth | 3.3 | 50.5 |
| 3 Months | 6.0 | 61.1 |
| 6 Months | 7.8 | 67.8 |
| 9 Months | 9.2 | 72.3 |
| 1 Year | 10.2 | 76.1 |
| 2 Years | 12.3 | 85.6 |
| 3 Years | 14.6 | 94.9 |
| 4 Years | 16.7 | 102.9 |
| 5 Years | 18.7 | 109.9 |
| 6 Years | 20.7 | 116.1 |
| 7 Years | 22.9 | 121.7 |
| 8 Years | 25.3 | 127.0 |
| 9 Years | 28.1 | 132.2 |
| 10 Years | 31.4 | 137.5 |
| 11 Years | 32.2 | 140.0 |
| 12 Years | 37.0 | 147.0 |
| 13 Years | 40.9 | 153.0 |
| 14 Years | 47.0 | 160.0 |
| 15 Years | 52.6 | 166.0 |
| 16 Years | 58.0 | 171.0 |
| 17 Years | 62.7 | 175.0 |
| 18 Years | 65.0 | 177.0 |
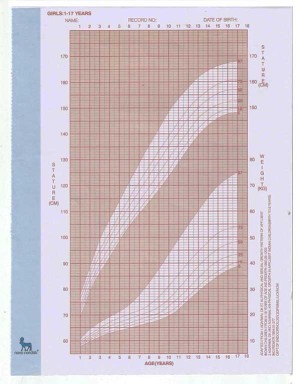
Average height and weight of girls at different ages
(Source : Nutrient Requirements and Recommended Dietary Allowances for Indians, I.C.M.R. 1990.)
| Age | Weight (kg) | Height (cm) |
| Birth | 3.2 | 49.9 |
| 3 Months | 5.4 | 60.2 |
| 6 Months | 7.2 | 66.6 |
| 9 Months | 8.6 | 71.1 |
| 1 Year | 9.5 | 75.0 |
| 2 Years | 11.8 | 84.5 |
| 3 Years | 14.1 | 93.9 |
| 4 Years | 16.0 | 101.6 |
| 5 Years | 17.7 | 108.4 |
| 6 Years | 19.5 | 114.6 |
| 7 Years | 21.8 | 120.6 |
| 8 Years | 24.8 | 126.4 |
| 9 Years | 28.5 | 132.2 |
| 10 Years | 32.5 | 138.3 |
| 11 Years | 33.7 | 142.0 |
| 12 Years | 38.7 | 148.0 |
| 13 Years | 44.0 | 150.0 |
| 14 Years | 48.0 | 155.0 |
| 15 Years | 51.5 | 161.0 |
| 16 Years | 53.0 | 162.0 |
| 17 Years | 54.0 | 163.0 |
| 18 Years | 54.4 | 164.0 |

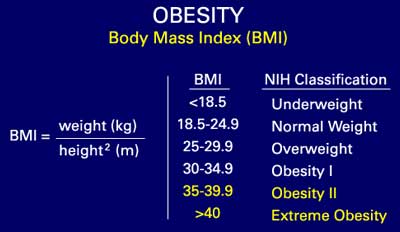
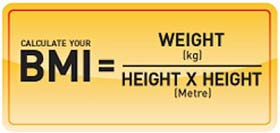 The ASHWIN SPECIALITY HOSPITAL Dietary clinic has the expertise to design a personalized menu to fit your needs, like and dislikes, lifestyle modifications and measures. The body mass index (BMI) or Quetelet index is a value derived from the mass (weight) and height of an individual. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is universally expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms and height in metres. The BMI is an attempt to quantify the amount of tissue mass (muscle, fat, and bone) in an individual, and then categorize that person as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese based on that value.
The ASHWIN SPECIALITY HOSPITAL Dietary clinic has the expertise to design a personalized menu to fit your needs, like and dislikes, lifestyle modifications and measures. The body mass index (BMI) or Quetelet index is a value derived from the mass (weight) and height of an individual. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is universally expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms and height in metres. The BMI is an attempt to quantify the amount of tissue mass (muscle, fat, and bone) in an individual, and then categorize that person as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese based on that value.